When you’re experiencing WiFi connectivity issues in your Tesla, it can disrupt several in-car functions such as navigation updates, music streaming, and over-the-air software updates that are vital for the optimal performance of your vehicle.
The convenience of having these services at your fingertips is one of the benefits of Tesla’s advanced technology, so a malfunctioning WiFi connection can be quite frustrating.
Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to diagnose and fix the problem, ensuring that your Tesla stays connected and up-to-date.
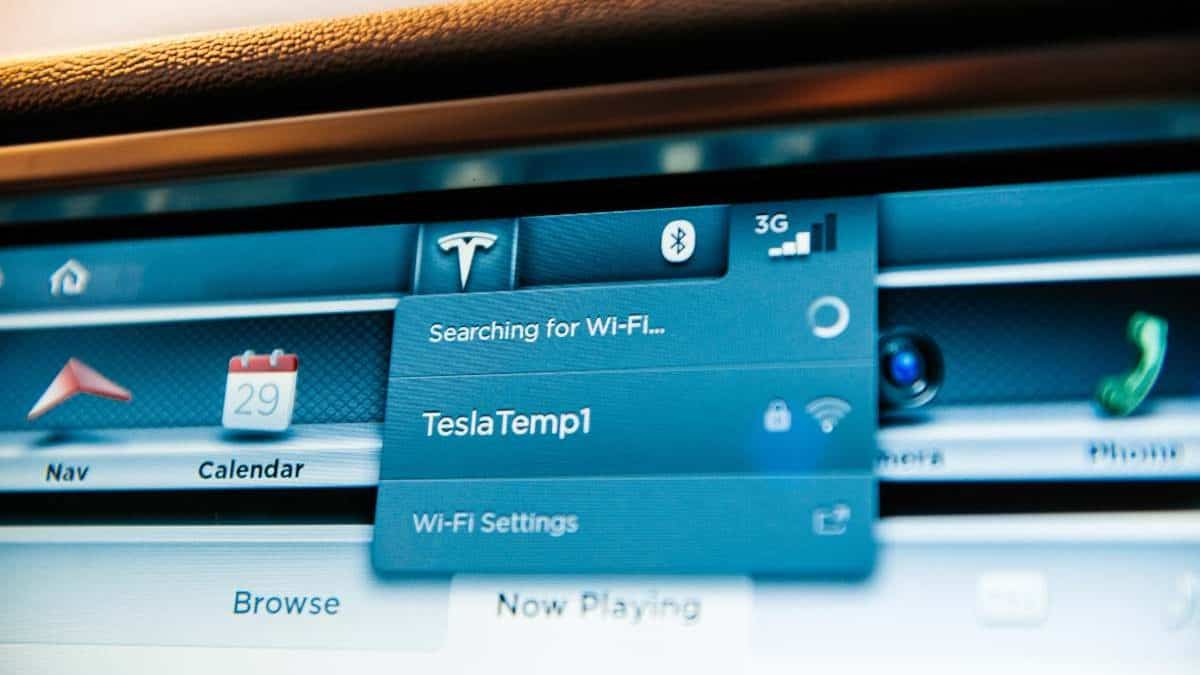
Connectivity problems can often be attributed to common issues like router malfunctions or incorrect network settings.
Before diving into more elaborate solutions, it’s a good idea to perform basic troubleshooting steps such as checking your router’s power and internet connection, ensuring your Tesla is within range of the signal, and verifying that your vehicle is connected to the correct network.
Advanced troubleshooting may involve looking into network security settings or considering possible interference sources. If these efforts don’t resolve the issue, Tesla Support offers assistance to help get your WiFi connection back on track.
Key Takeaways
- Performing basic troubleshooting can resolve common WiFi issues.
- Advanced network settings might require fine-tuning for optimal connectivity.
- Tesla Support is available for persistent connectivity challenges.
Understanding Wi-Fi Connectivity in Tesla Vehicles
Your Tesla’s ability to connect to Wi-Fi is essential for accessing streaming services, receiving software updates, and providing a better overall user experience.
This connectivity depends on several components and is subject to various factors that can affect its functionality.
Wi-Fi Components and Functionality
Your Tesla vehicle’s Wi-Fi connectivity relies on an antenna that’s designed to connect to available Wi-Fi networks.
This antenna allows your car to communicate with your home network or public hotspots, typically supporting both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies for a more reliable connection.
The control of this function is easily accessible through the touchscreen, where you can scan for networks, input passwords, and view signal strength.
Regular software updates are delivered over Wi-Fi, facilitating improvements and new features for your Tesla.
Common Wi-Fi Connection Issues
Despite the advanced Wi-Fi capabilities, you may encounter weak signal issues or interference that disrupts connectivity.
Some common factors leading to a poor Wi-Fi connection include the distance between your vehicle and the router, obstacles that impede signal strength, and interference from other electronic devices.
If your Tesla’s Wi-Fi is not working correctly, troubleshooting steps involve checking the Wi-Fi network on other devices, restarting your Tesla’s touchscreen, or moving your vehicle closer to the access point for a stronger signal.
For persistent connection problems, optimizing your home network settings or utilizing recommended Wi-Fi extenders may improve your experience.
Initial Troubleshooting Steps
When your Tesla’s Wi-Fi isn’t connecting, it’s essential to perform a series of initial troubleshooting steps. These will help identify whether the issue lies with your home Wi-Fi network, the vehicle’s software, or the car’s touchscreen.
Checking Your Wi-Fi Network
Ensure that your Wi-Fi router is powered on and you are within range. Your Tesla should display the SSID of your network in the list of available connections.
Verify that your network settings are correct, including the SSID and security password. Check other devices to see if they can connect. If not, the problem might be with your router or DHCP server.
Ensuring Tesla Software is Up-to-Date
Occasionally, software updates may fix bugs that cause connectivity issues. Check for available Tesla updates in the ‘Software’ section of your vehicle’s control screen.
Ensure that your car’s software version is current as new updates often include improvements to functionality including Wi-Fi connectivity.
Rebooting Vehicle’s Touchscreen
A system reboot can resolve transient issues with your Tesla’s systems. To reboot the touchscreen, press and hold down both scroll buttons on the steering wheel until the screen goes dark and the Tesla logo appears.
Rebooting does not erase any of your personal settings, but it can fix temporary glitches including Wi-Fi connectivity problems.
Remember, these steps are often effective at resolving common Wi-Fi connection issues with your Tesla. If these don’t work, further technical troubleshooting may be necessary.
Advanced Wi-Fi Troubleshooting
When your Tesla’s Wi-Fi connectivity falls short, there are advanced steps you can take to resolve signal strength problems and mitigate Wi-Fi network interference. The following subsections provide focused guidance for these specific challenges.
Resolving Signal Strength Issues
If you’re experiencing a weak signal, the first thing you should check is the proximity of your Tesla vehicle to the Wi-Fi router.
Wi-Fi signal strength diminishes with distance and barriers like walls, so parking closer to the router can significantly improve your connection.
Moreover, if you have a 5 GHz network, it may offer faster speeds but has a shorter range than a 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi network. Consider switching to 2.4 GHz if your Tesla is parked farther away.
In cases where moving the car or router isn’t practical, using a Wi-Fi extender can bridge the gap.
Wi-Fi extenders effectively boost the existing signal to reach your Tesla, offering a more reliable connection for over-the-air updates and streaming services like Netflix.
Dealing with Wi-Fi Network Interference
Interference can be a significant impediment to your Tesla’s Wi-Fi connection. Devices such as microwaves, cordless phones, and even DLNA servers can cause disruption since they operate within the same frequency bands as your Wi-Fi network.
To combat this, identify and turn off devices that could be interfering or try changing the channel on your router. Most routers automatically pick a channel; however, manually selecting a less crowded channel can lead to less interference.
Using devices that support 5 GHz Wi-Fi can alleviate some of these issues as this band is typically less congested than 2.4 GHz.
Remember, networks operating on 5 GHz frequencies are not only faster but are also less susceptible to interference, making them a suitable choice for environments with many competing signals.
Wi-Fi Connectivity Features and Limitations

Tesla vehicles offer robust Wi-Fi connectivity that supports various in-car features. It is critical for you to understand its capabilities and the restrictions you may encounter when connecting to networks outside the Tesla ecosystem.
Wi-Fi Usage Within Tesla Ecosystem
Tesla vehicles are designed to remain connected to Wi-Fi even while in drive mode, allowing you to enjoy features such as maps, music, and web browsing seamlessly.
Your Tesla can connect to both 2.4 GHz and, depending on the model, 5 GHz Wi-Fi networks to facilitate high-speed internet access.
This connectivity is crucial for over-the-air software updates, accessing Tesla’s vast entertainment options such as Netflix, and for general web browsing.
However, it’s important to note that the car must be parked to enjoy certain streaming services.
- Maps: Your Tesla uses Wi-Fi to download detailed maps for navigation.
- Music/Web: Stream music or browse the web while connected to Wi-Fi.
- Netflix: Watch your favorite shows when parked with a good Wi-Fi connection.
Restrictions and Connectivity Beyond Tesla Network
While your Tesla can connect to public Wi-Fi networks, limitations do exist, especially regarding VPN connections and UDP timeouts.
A VPN can help secure your data over a public network, but you might experience issues such as increased UDP timeouts, leading to potential difficulties in maintaining a stable connection.
Furthermore, while Tesla’s LTE cellular connection is an alternative when Wi-Fi is not available, it is not a replacement for a strong Wi-Fi signal, and the transition between LTE and Wi-Fi can sometimes result in a temporary loss of connectivity.
- VPN: Potential issues with maintaining VPN connections on public networks.
- UDP: Increased UDP timeouts can occur over VPN, affecting connectivity.
- LTE/Cellular Connection: A fallback option, but not as reliable as a dedicated Wi-Fi connection for streaming and updates.
Advanced Network Options and Security
Optimizing your Tesla’s Wi-Fi connectivity involves not just connecting to a network but ensuring security through advanced settings and extending reach via configuring additional networks and extenders.
Enhancing Security with Advanced Settings
When you secure your vehicle’s Wi-Fi connection, it’s crucial to choose robust encryption protocols.
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA and WPA2) are currently the most secure, whereas Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is deemed less secure due to known vulnerabilities.
Be sure to select WPA2 in your router’s settings for a robust defense.
- SSID and Hidden Networks: Your network name (SSID) can be visible or hidden. If you opt to hide your SSID for additional secrecy, you’ll need to enter it manually into your Tesla’s network settings.
- MAC Address Filtering: Implementing MAC address filtering adds an extra layer of security. Only devices with approved MAC addresses will be granted access.
Configuring Wi-Fi Extenders and Additional Networks
To ensure your Tesla maintains a strong connection, consider the following:
- Extenders: A Wi-Fi extender can boost your network’s range, particularly useful if your Tesla is parked at a considerable distance from the router. Both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz options are available; choose one that matches your vehicle’s capabilities.
- Settings for Extenders: Some extenders offer separate network names (SSIDs), while others extend your existing SSID. Confirm these details before setup.
- Dual-Band Frequencies: Vehicles may connect more reliably to 2.4 GHz due to its wider range, despite 5 GHz offering faster speeds. Evaluate your parking area and decide accordingly.
- Forget Network: If you ever need to troubleshoot or prefer to switch networks, use your Tesla’s “Forget Network” option to reset the Wi-Fi connection and address any persistent security issue.
Tesla Support and Service Options
If you’re experiencing issues with your Tesla’s WiFi connection, it’s essential to be aware of the dedicated Tesla support and available service options.
Whether you encounter an error message or need hands-on assistance, Tesla is equipped to offer guidance and solutions.
When to Contact Tesla Support
You should reach out to Tesla Support if you see any error message concerning your WiFi connectivity or if standard troubleshooting steps fail. Here are situations where contacting Tesla Support is recommended:
- An error message appears repeatedly, hindering your Tesla’s WiFi connection.
- Your Model S, Model 3, Model X, or Model Y fails to connect to known networks after attempting basic troubleshooting.
To contact Tesla Support:
- Use your Tesla Mobile App.
- Choose ‘Service’ from the options.
- Tap ‘Schedule Service’ and then select ‘Connectivity’ as the issue.
Utilizing Service Centers and Superchargers
Tesla Service Centers can provide in-person support with WiFi connection issues. Tesla technicians can assess and resolve problems that might not be apparent remotely.
Additionally, at Superchargers, you can often find helpful information or assistance from the staff or through posted guidelines, specifically for Model S, Model 3, Model Y, and Model X vehicles.
To utilize service centers or superchargers:
- Find the nearest Service Center through your Tesla Mobile App.
- Visit the center, and Tesla’s trained professionals will assist you with your vehicle’s WiFi issues.
- While Superchargers are primarily for charging, there could be network information applicable to your connectivity issues.
- Tesla Charger Installation Cost (Home Setups) - March 1, 2024
- Tesla Phone Key Disconnected (Troubleshooting Guide and Quick Fixes) - March 1, 2024
- Tesla FSD 12 (Explained) - March 1, 2024