As the world strives to reduce air pollution and mitigate climate change, Partial Zero Emission Vehicles (PZEVs) have emerged as an eco-friendly driving solution.
But what exactly is a PZEV, and how does it differ from other low-emission vehicles? Most importantly, can driving these cars truly make a positive impact on our environment? Through this blog post, we’ll explore the ins and outs of PZEVs, examining their benefits and challenges along with their contribution in reducing emissions for a greener and healthier future.

RL GNZLZ from Chile, CC BY-SA 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Key Takeaways
- Partial Zero Emission Vehicles (PZEVs) are gas-powered cars that use advanced engineering techniques to achieve zero evaporative emissions from their fuel systems, and in addition, meet strict “Super Ultra Low Emission Vehicle” (SULEV) tailpipe emission standards.
- The warranty on the components of the emissions system must be for the expected life of the vehicle, i.e. 15 years or 150,000 miles.
- Compared to traditional gas-powered vehicles, PZEVs emit up to 90% less smog-forming pollutants.
- PZEVs offer cost savings for consumers over time due to their warranties on emission control parts, and potentially qualifying for state incentives or tax credits. However, challenges in implementing the technology remain, such as higher upfront costs.
Understanding Partial Zero Emission Vehicles (PZEVs)
A PZEV is a gas-powered vehicle that achieves ultra-low emissions and meets strict SULEV tailpipe and evaporative emission standards.
What Is A PZEV?
As mentioned above, a PZEV, or partial zero emission vehicle, is a gasoline-powered car designed to meet strict emissions standards and reduce its impact on the environment.
These vehicles are considered some of the cleanest-running gas-powered cars available in terms of air pollution, and were initially developed to satisfy California’s rigorous air quality regulations.
In order to achieve these milestones, PZEVs come equipped with advanced features without sacrificing performance or relying on alternative fuels.
Some notable enhancements include:
 | Anti-permeation fuel system liners to prevent off-gassing. |
 | Carbon air intake filters that stop fuel vapors from leaking out. |
 | Close-coupled catalytic converters lined with precious metals that eliminate nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide. |
 | Carbon canister scrubbers installed in the fuel line for additional filtration. |
 | Special fuel injectors that don’t cause evaporative emissions from fuel leakage. |
 | Engine control module (ECM) to delay ignition timing, allowing the catalytic converter to heat up sooner. |
 | Dual-filtration air-intake system to stop evaporative hydrocarbons from escaping through the engine’s air intake. |
Brief History of Partial Zero Emission Vehicles
Partial Zero Emission Vehicles were first created as an administrative category of vehicle in 1998 by the California Air Resources Board (CARB).
The category came about as a way to make it more realistic for automakers to meet California’s requirements to sell a minimum number of Zero Emission Vehicles (ZEV), i.e. electric or hydrogen cars.
Car manufacturers at the time were not equipped to produce enough ZEVs, so they were awarded credits toward their ZEV sales targets for their sales of this new much cleaner category of car.
PZEVs began to be sold in the state of California, as well as the other six “clean-car states” at that time (the states that had adopted the stricter California emissions regulations over the federal emissions regulations): Maine, Massachusetts, New York, Oregon, and Vermont.
Since then, the list of “clean-car” states has approximately tripled, and in the present day, PZEVs are widely available for sale throughout the United States.
PZEV Automakers And Models
PZEV cars are actually more common than you might realise, being manufactured by well known brands such as Ford, Subaru, Mazda, and Honda.
Here’s a small table of some of the most popular PZEVs on the market:
 | Subaru Forester |
 | Subaru Outback |
 | Honda Civic |
 Dinkun Chen, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons | Mazda 6 |
 Rudolf Stricker, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons | Ford Focus |
PZEV Standards And Requirements
To meet the stringent PZEV standards and requirements, vehicles must go through a rigorous certification process. First and foremost, these cars need to achieve zero evaporative emissions – this means no fuel vapors are released from the vehicle’s gas tank or fuel system.
One of the reasons PZEVs were developed was to help automakers comply with California’s strict CARB air quality regulations. As a result, manufacturers equip these vehicles with advanced technologies such as anti-permeation fuel system liners, carbon air intake filters, carbon canister scrubbers, and close-coupled catalytic converters to prevent harmful emissions from escaping into the atmosphere.

How Are PZEVs Different From Other Low-emission Vehicles?
One key difference between PZEVs and other low-emission vehicles is the way they achieve their emission reductions. While hybrid or electric vehicles rely on battery technology to minimize or eliminate tailpipe emissions, PZEVs employ various advanced engineering techniques in conjunction with a standard gas-powered engine.
As an example, let’s compare Partial Zero Emission Vehicles to Super Ultra-Low Emission Vehicles (SULEV). Both types of cars meet strict emissions standards but still utilize gasoline engines.
The primary difference lies in their evaporative emissions control systems: A SULEV might have some evaporative emissions from its fuel tank while a PZEV is designed to have zero evaporative emissions.
Another distinction between PZEVs and other environmentally-friendly vehicles like hybrids or fully electric ones is performance. Unlike many alternative-fuel options that often sacrifice power for reduced environmental impact, a Partial Zero Emissions Vehicle maintains comparable levels of performance without compromising on efficiency or pollution reduction.
Environmental Benefits Of PZEVs
PZEVs offer numerous benefits to the environment, including significantly reducing smog and air pollution, leading to improved air quality and public health.
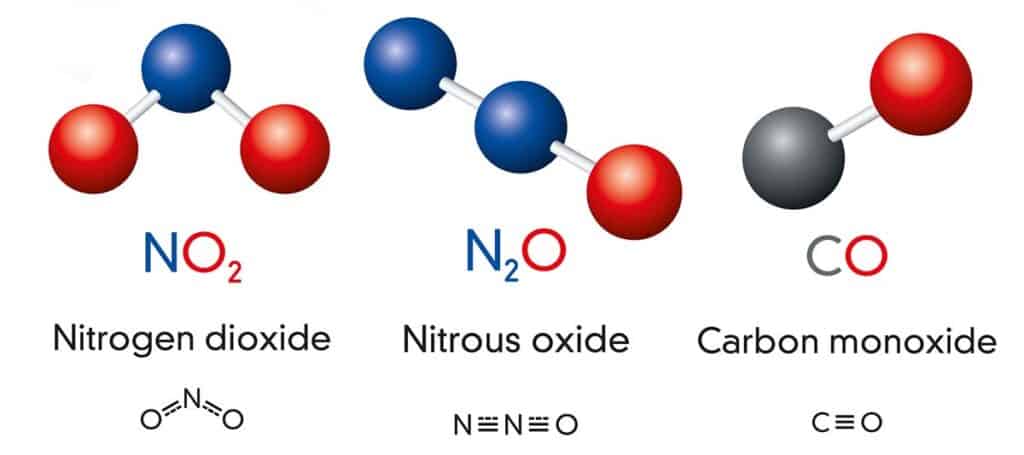
Reduction In Smog Forming Emissions And Air Pollution
One of the primary benefits of Partial Zero Emission Vehicles (PZEVs) is their significant reduction in air pollution emissions. PZEVs use advanced emission control technologies to eliminate or reduce harmful pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides, nitrogen dioxide, and carbon monoxide, which are pre-cursors to smog.
This results in cleaner air and a reduction in smog- and acid rain-producing emissions. Compared to traditional gas-powered vehicles, PZEVs emit up to 90% less smog-forming pollutants.
Improved Air Quality And Public Health
One of the most important aspects to consider is how Partial Zero Emission Vehicles impact public health. PZEVs are designed to emit fewer pollutants than traditional gas-powered vehicles, and this reduction has multiple beneficial effects on air quality and human health.
Additionally, reduced emissions also mean improved public health outcomes. Exposure to air pollution increases susceptibility to asthma attacks and other lung-related issues such as pneumonia and bronchitis.
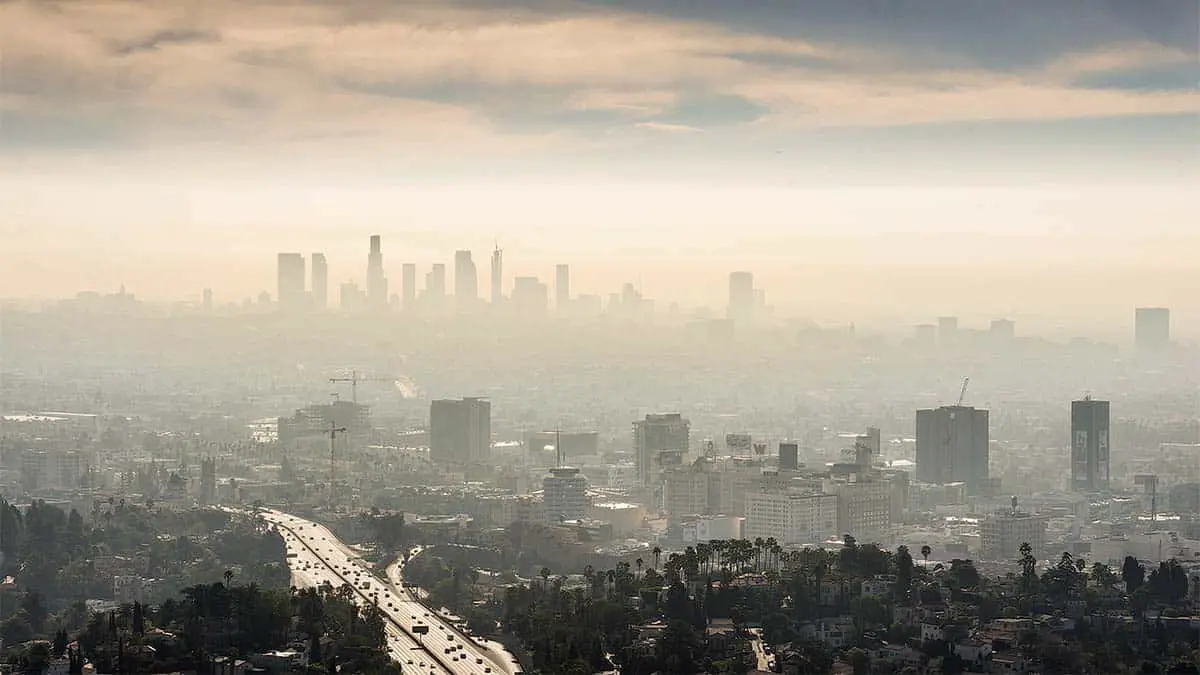

Comparing PZEVs To Traditional Gas-powered Vehicles
In this section, we compare PZEVs to traditional gas-powered vehicles to better understand their benefits and impact on the environment.
| Aspect | Partial Zero Emission Vehicles (PZEVs) | Traditional Gas-Powered Vehicles |
|---|---|---|
| Emission Standards | PZEVs meet strict emissions standards, including zero evaporative emissions and SULEV tailpipe emissions. | Traditional vehicles often emit higher levels of pollutants and do not adhere to the same strict emissions standards. |
| Warranty | PZEVs have warranties on their emission control parts that last for 15 years or at least 150,000 miles. | Warranties for emission control parts in traditional vehicles may not be as extensive as PZEVs. |
| Environmental Impact | PZEVs result in a 90% or more decrease in smog- and acid rain-producing emissions compared to standard combustion vehicles. | Traditional gas-powered vehicles contribute significantly to air pollution and climate change due to higher emissions. |
| Performance | PZEVs offer smog reduction without a decrease in performance, maintaining the same driving experience as traditional vehicles. | While traditional vehicles may have similar performance, they often do so at the cost of increased emissions and pollution. |
| Fuel System | PZEVs have anti-permeation fuel system liners, carbon air intake filters, carbon canister scrubbers, and close-coupled catalytic converters to prevent emissions. | Traditional vehicles often lack the advanced emission reduction technologies found in PZEVs, leading to higher emissions. |
By comparing PZEVs to traditional gas-powered vehicles, we can see the significant benefits of PZEV technology in reducing emissions and improving air quality, while still maintaining comparable performance and driving experience.
Advantages And Challenges Of PZEVs
PZEVs offer long-term cost savings and environmental benefits for consumers, but challenges remain in implementing the technology and making them widely available and affordable.
Cost Savings And Long-term Benefits For Consumers And The Environment
As consumers, we often think about the upfront costs of purchasing a vehicle without considering the long-term benefits. The good news is that PZEVs not only help the environment but also offer significant cost savings over time.
Since PZEVs have warranties on their emission control parts for up to 15 years or at least 150,000 miles, there are fewer maintenance costs associated with these vehicles compared to traditional combustion engines.
Another consideration is the fact that PZEVs do not require alternative fuels like other low- or zero-emission vehicles, you can just fill up at any gas station.
Challenges In Implementing PZEV Technology
Implementing PZEV technology is challenged a number of ways, including:
- Cost: PZEVs are generally more expensive to purchase than standard combustion vehicles due to the additional emissions-control technology needed.
- Limited availability: While major automakers such as Subaru, Mazda and Honda offer PZEVs in some areas, they may not be available in all locations.
- Lack of consumer awareness: Many consumers are still unaware of the benefits offered by PZEVs, which can limit demand for them.
- Technology constraints: Some types of engines may not be compatible with PZEV technology or may require significant modifications to achieve compliance.
- Testing and certification issues: Manufacturers must go through extensive testing and certification processes to ensure their vehicles meet PZEV requirements, which delays production and increases costs.
- Maintenance requirements: The specialized emissions-control components used in PZEVs often require specialized maintenance procedures that can be more costly than traditional vehicle maintenance.

Availability And Affordability Of PZEVs
As PZEVs have become more popular and mainstream, they are now available in most states and made by major brands such as Subaru, Mazda, Honda, Ford, and Volkswagen.
This means that consumers have more options when it comes to choosing a clean-running vehicle that meets strict emissions standards. However, affordability remains a challenge for many people interested in purchasing a PZEV.
These vehicles often come with an initial higher price tag than traditional gas-powered cars but can save drivers money over time through reduced maintenance costs.
Additionally, some states offer incentives or tax credits for purchasing eco-friendly vehicles like PZEVs which can help offset the upfront cost for consumers.
The Future Of PZEVs And Their Role In Reducing Emissions
PZEVs will play a crucial role in reducing emissions as we transition to a more sustainable transportation system, serving as a stepping stone towards fully zero-emission vehicles.
PZEVs As A Stepping Stone To Fully Electric Vehicles
As we work to reduce vehicle emissions and improve air quality, PZEVs are a vital part of the transition toward fully zero-emission vehicles. These cars provide a cleaner alternative to traditional gas-powered vehicles while still using gasoline as their primary fuel source.
PZEV technology allows us to make incremental progress towards reducing emissions while giving automakers time to develop sustainable solutions that can replace fossil fuels entirely.

The Importance Of Continued Innovation In Sustainable Transportation.
As we look towards the future, it becomes clear that continued innovation in sustainable transportation is critical to reducing emissions and protecting our environment.
Innovations like these will be key to creating a cleaner, more sustainable future where individuals can enjoy the freedom of personal transportation without contributing significantly to air pollution.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a Partial Zero Emission Vehicle (PZEV) is a gas-powered car that meets the strictest emissions standards with zero evaporative emissions and SULEV tailpipe emissions.
PZEVs offer immense environmental benefits such as reducing smog forming emissions and improving public health by reducing air pollution.
Although there are challenges in implementing PZEV technology, such vehicles have cost savings for consumers over time and play an important role in reducing overall vehicle emissions.
FAQs:
How does a PZEV help the environment?
By emitting fewer harmful pollutants and gases, PZEVs help reduce air pollution levels in cities, improve overall air quality, and promote public health.
Are there any downsides to owning a PZEV?
While PZEVs are generally considered more environmentally friendly than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, they may come with some trade-offs such as slightly reduced power or acceleration due to their advanced emission control systems. Additionally, they may require specialized maintenance procedures or components that can be more expensive than those found in traditional vehicles.
Where can I find information on PZEV models available for purchase?
Most major car manufacturers offer several models of PZEV vehicles in their lineup today. Consumers can typically find information about these models online through manufacturer websites or consumer resource platforms dedicated to green vehicles and sustainability initiatives like Green Car Journal or Green Car Reports.
Are hybrids considered PZEVs?
No, hybrids and plug-in hybrids are not considered to be PZEVs because they are in the Low Emission Vehicle (LEV) and Electric Vehicle (EV) category. The definition of PZEV only contemplates gas-powered cars with no evaporative emissions, and that meet SULEV tailpipe emissions.
- Tesla Charger Installation Cost (Home Setups) - March 1, 2024
- Tesla Phone Key Disconnected (Troubleshooting Guide and Quick Fixes) - March 1, 2024
- Tesla FSD 12 (Explained) - March 1, 2024