As global awareness of environmental issues increases, the concept of low emission vehicles is becoming more relevant and essential than ever before. But what exactly are these eco-friendly alternatives to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles? In this blog post, I’ll explore low emission vehicles (LEVs), discussing their importance for both the environment and public health.

Key Takeaways
- Low emission vehicles (LEVs) are cars, trucks or buses that produce fewer pollutants and greenhouse gases than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. They use advanced technologies to reduce emissions like electric drivetrains, hydrogen fuel cells, and hybrid systems.
- LEVs are important for the environment because they can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve air quality, conserve natural resources, and provide public health benefits by reducing toxic pollutants released into the atmosphere.
- There are four main types of low emission vehicles: Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs), Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), and Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs).
- Although there may be higher upfront costs associated with buying an LEV compared to a traditional gasoline-powered vehicle, long-term savings on fuel and maintenance coupled with government incentives make them an increasingly attractive option for consumers looking to live more sustainably.
Low Emission Vehicles (LEV) Explained
Low Emission Vehicles (LEV) are cars, trucks or buses that produce fewer pollutants and greenhouse gases than traditional gasoline vehicles. They use advanced technologies like electric drivetrains, hydrogen fuel cells, and hybrid systems to reduce emissions.
The term “low emission vehicle” originates from the state of California’s Low Emission Vehicle Program, initiated in 1990 and which has evolved to the present day with ever tougher emissions requirements for all vehicles on California’s roads.
Definition And Types Of LEVs
As someone who is well-versed in vehicle emissions laws, I understand the confusion people often experience when they come across terms like “low emission vehicle” or LEV.
Let me break it down for you in simple terms. A low emission vehicle (LEV) is a car or truck that produces significantly lower levels of harmful pollutants compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
Now, let’s talk about some different types of low emission vehicles available today. They are classified by the level of tailpipe emissions produced, with each category having specific requirements set forth by regulatory agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the California Air Resources Board (CARB).
Examples include Transitional Low Emission Vehicles (TLEVs), Ultra-Low Emission Vehicles (ULEVs), Super Ultra-Low Emission Vehicles (SULEVs), Partial Zero-Emission Vehicles (PZEVs), Advanced Technology PZEVs (AT PZEVs), and finally, Zero-Emission Vehicles(ZEVs).
Hybrid-electric vehicles typically fall under AT PZEV classification which showcases impressive fuel efficiency while producing very minimal pollution.

How Do Low Emission Vehicles Work?
Low emission vehicles, or LEVs, employ a variety of advanced technologies and design features to significantly reduce harmful emissions compared to traditional gasoline vehicles.
One key element in reducing emissions is the use of more efficient engines that burn fuel more completely, resulting in fewer pollutants being released into the atmosphere.
In addition to engine improvements, low emission vehicles often incorporate systems for capturing and treating exhaust gases before they are released from the tailpipe.
This can include components such as three-way catalytic converters that convert harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and hydrocarbons (HC) into less toxic substances like water vapor and carbon dioxide.
Let’s take hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) as an example – these cars combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor for propulsion. The battery-powered electric motor not only enhances overall performance but also lowers emissions by allowing the car to run on electricity during lower-speed city driving when most pollution occurs.
When needed, the internal combustion engine kicks in at higher speeds or under heavy acceleration demands where it operates more efficiently than smaller engines found in other low emitting vehicles.
Comparison To Traditional Gasoline Vehicles
When comparing low emission vehicles to traditional gasoline vehicles, it’s important to consider the environmental and health benefits, as well as differences in performance and costs. The following table provides a side-by-side comparison of these important factors:
| Factors | Traditional Gasoline Vehicles | Low Emission Vehicles |
|---|---|---|
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Higher emissions contribute to climate change and air pollution. | Significantly reduced emissions help combat climate change and improve air quality. |
| Air Quality | Emit pollutants such as nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and particulate matter, which contribute to smog and poor air quality. | Lower emission levels result in improved air quality and reduced smog formation. |
| Fuel Efficiency | Relative to vehicle size and type, fuel efficiency can vary widely; however, overall fuel efficiency is generally lower than that of LEVs. | Typically more fuel-efficient than traditional gasoline vehicles, with some types consuming little to no gasoline (e.g., BEVs). |
| Performance | Traditional engines can offer strong performance; however, they may be less efficient and emit more pollutants. | Many LEVs, such as hybrids and electric vehicles, offer comparable or superior performance, with the added benefit of fewer emissions and greater efficiency. |
| Cost | Initial purchase price and fuel costs may be lower, but long-term costs related to maintenance and environmental impact can be significant. | While initial purchase prices may be higher, tax incentives, rebates, and long-term savings on fuel and maintenance can offset these costs. |
| Government Policies & Incentives | Subject to EPA and local emission regulations, which are becoming more stringent over time. | Often benefit from tax incentives, rebates, and other policies aimed at promoting the adoption of cleaner transportation options. |
While low emission vehicles may have higher upfront costs, they offer significant environmental and health benefits, as well as long-term savings on fuel and maintenance. As government policies and incentives continue to promote cleaner transportation options, the adoption of low emission vehicles will play a crucial role in reducing our impact on the environment.
Importance Of Low Emission Vehicles For The Environment
Low emission vehicles are crucial for the environment because they can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve air quality, conserve natural resources, and provide public health benefits.
Reduction In Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Low Emission Vehicles (LEV) play an essential role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and slowing down the effects of climate change. LEVs generate fewer pollutants, including carbon dioxide, which is the main contributor to global warming.
For instance, Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) produce zero tailpipe emissions during operation, making them a reliable source of low-emission transportation. According to research by the Union of Concerned Scientists, driving a BEV emits about 54% less greenhouse gases than driving a traditional gasoline vehicle over its lifetime.
Keywords: Low Emission Vehicles, Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Carbon Footprint

Improved Air Quality
Breathing in polluted air can have serious health consequences, particularly for people with pre-existing conditions like asthma and heart disease. Low emission vehicles are an essential tool to help improve air quality by reducing harmful pollutants from vehicle exhausts.
Nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide and particulate matter all contribute to poor air quality and can lead to respiratory illness or worse.
For example, the EPA estimates that a single BEV could save over 15 tons of carbon dioxide emissions per year compared to a traditional gasoline vehicle.
This translates into cleaner air, reduced greenhouse gas emissions leading to lower atmospheric temperature increases, healthier communities near busy roads and improved public health overall.
Conservation Of Natural Resources
Another important reason why low emission vehicles are essential for the environment is because they can help reduce our dependence on non-renewable resources. Traditional gasoline-powered cars rely on fossil fuels, which contribute significantly to air pollution and other environmental problems.
Low emission vehicles, on the other hand, have the potential to reduce our dependence on these non-renewable resources by using alternative power sources like electricity or hydrogen fuel cells.
This shift towards renewable energy not only helps to protect our planet but also ensures that future generations will have access to clean and sustainable sources of energy.
Benefits For Public Health
As a public health concern, vehicle emissions play a crucial role in our society.
Low emission vehicles offer a solution to this problem by reducing the total amount of toxic pollutants that are released into the atmosphere.
In areas where LEVs make up a significant percentage of vehicles on the road, there is less smog and particulate matter pollution than in communities with higher levels of gasoline or diesel-powered cars.
Types Of Low Emission Vehicles
There are four main types of low emission vehicles, including Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs), Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), and Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs).
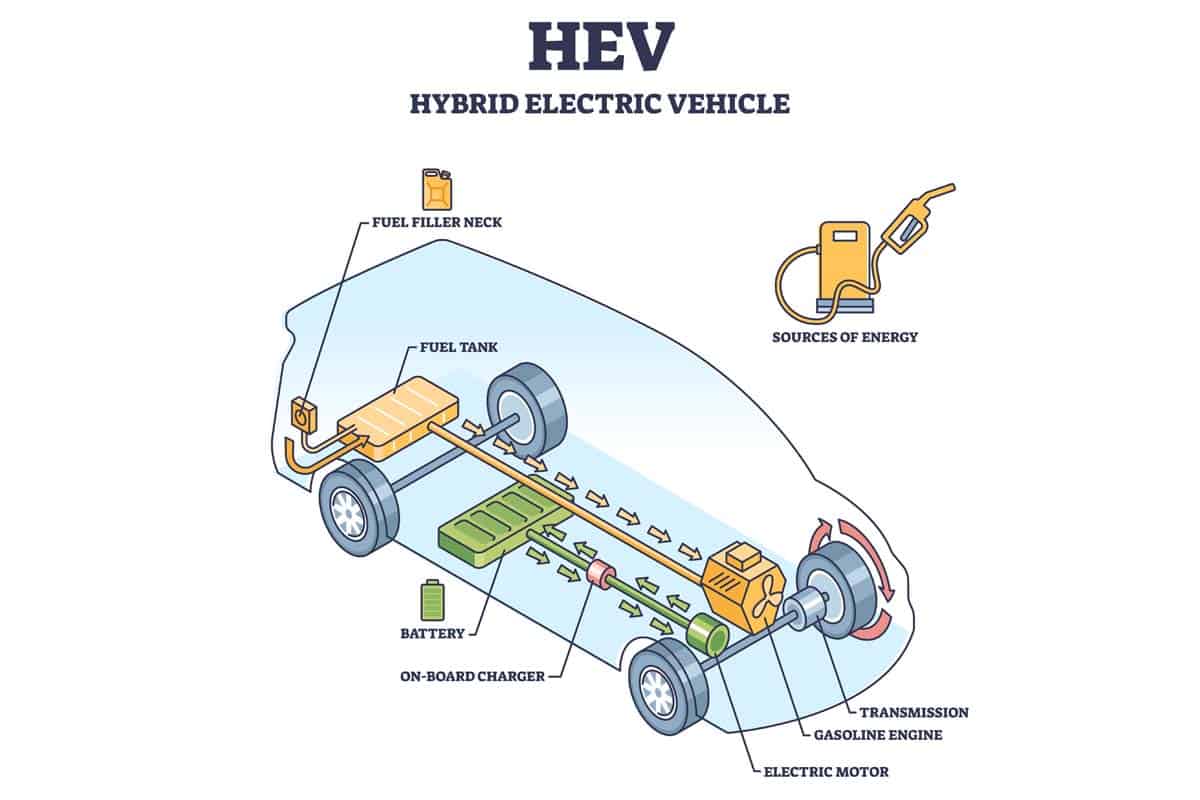
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
I personally believe that Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) are a great option for those looking to reduce their carbon footprint without sacrificing performance. HEVs use both an electric motor and an internal combustion engine, which work together to maximize fuel efficiency and minimize emissions.
Not only do HEVs emit significantly less greenhouse gases than traditional gasoline vehicles, they also save drivers money on gas. In fact, some models can achieve up to 50 miles per gallon or more.
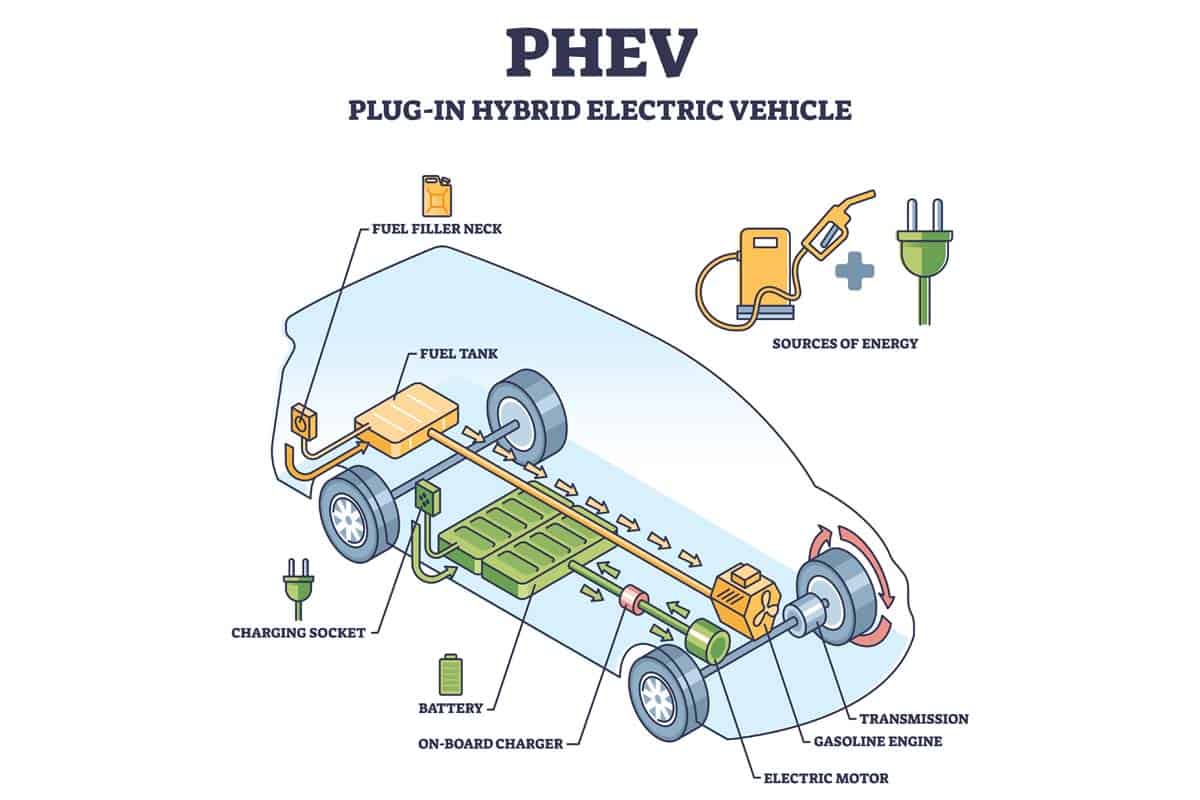
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs)
I find Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) to be a fascinating category of low emission vehicles. These cars use both an electric battery and gasoline engine, allowing for longer driving ranges than other types of electric vehicles.
The battery in a PHEV can be charged by plugging it into an outlet, or through regenerative braking while driving.
One example of a popular PHEV is the Toyota Prius Prime, which has an all-electric range of 25 miles before switching over to its gas engine. This means that for shorter commutes or errands, the car can operate entirely on electricity and emit zero tailpipe emissions.
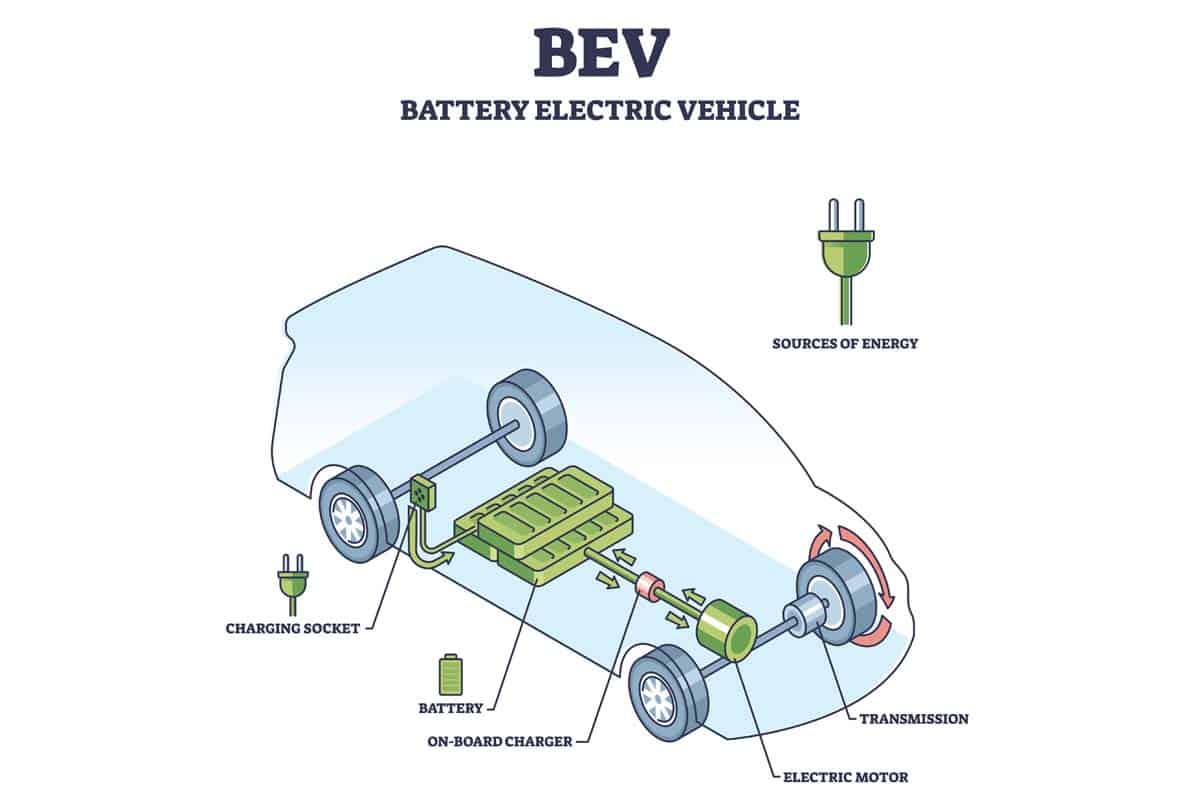
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
I own a Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) and I can tell you firsthand that it is an incredible feeling to drive with zero emissions. BEVs are powered entirely by electricity stored in large batteries, which means they produce no harmful tailpipe emissions.
They are categorized under the Zero-Emissions Vehicle (ZEV) classification because of their complete absence of pollution during operation. Not only are BEVs better for the environment than traditional gasoline vehicles, but they are also cheaper to operate in the long run since electricity is less expensive than gasoline.
Plus, many states offer incentives such as rebates or access to carpool lanes for drivers who choose low emission vehicles like BEVs.
According to important facts about low emission vehicles, BEVs produce zero harmful tailpipe emissions and are 98% cleaner than the average new model-year vehicle.
This makes them incredibly important for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution while conserving natural resources and benefiting public health.
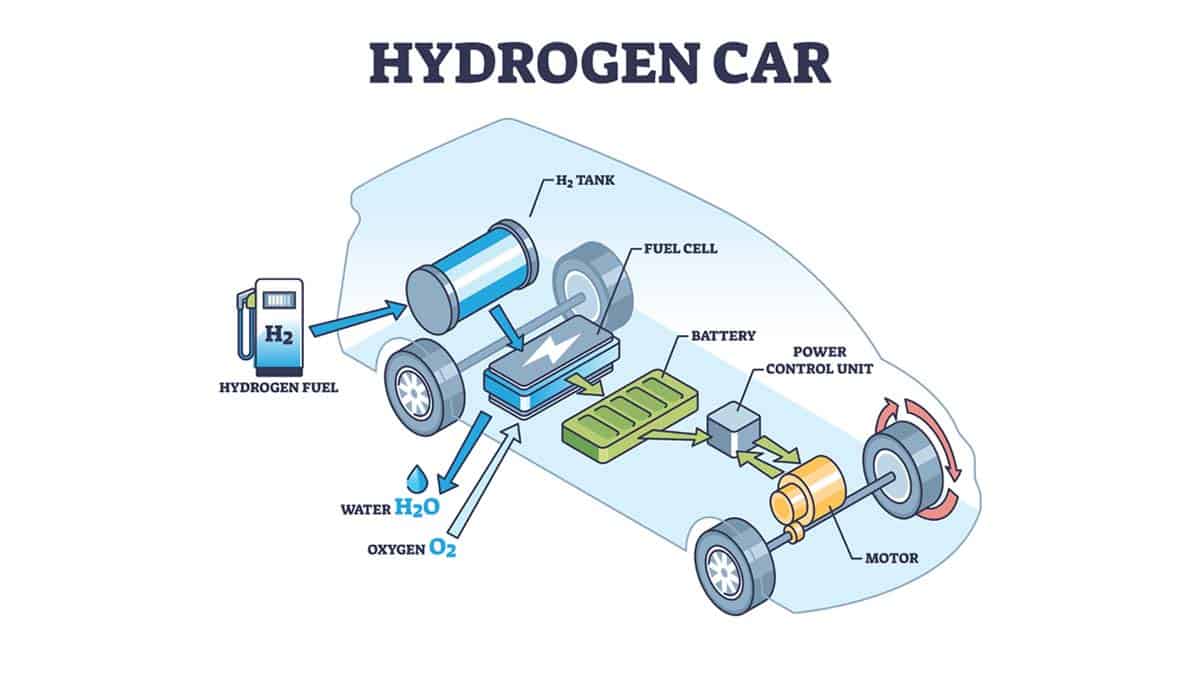
Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs)
Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs) are a type of Low Emission Vehicle (LEV) that run on hydrogen and oxygen, producing only water and heat as byproducts. This makes FCVs extremely important for the environment since they have zero harmful tailpipe emissions.
Although FCVs are still new to the market and not yet widely available, they have a lot of potential in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. One example is Toyota’s Mirai, which has a range of about 300 miles per tank and can be refueled in around five minutes.
Government Policies And Incentives For Promoting Low Emission Vehicles
Government regulations such as tax incentives, rebates and public awareness campaigns have been implemented to promote the use of low emission vehicles.
Regulations And Standards
Regulations and standards play a significant role in promoting low emission vehicles. The government has set stringent emission standards, such as LEV, ULEV, and SULEV, for automakers to follow to ensure that the new cars sold produce lower emissions.
Additionally, the government offers tax incentives and rebates to encourage people to purchase low-emission vehicles. In California, the ZEV mandate requires automakers to sell more zero-emission vehicles by 2025.
Moreover, the LEV III regulations require increasingly stringent emission standards for criteria pollutants and greenhouse gases for new passenger vehicles through 2025.
Public Awareness Campaigns
As an effort to promote low emission vehicles, public awareness campaigns have been launched to educate consumers about the benefits of these types of vehicles. Here are some ways public awareness campaigns are being used:
- Auto Shows: Car manufacturers showcase their newest low-emission vehicle models at auto shows around the world.
- Education Programs: Colleges and universities offer courses and seminars that focus on alternative fuel options, including electric and hybrid vehicles.
- Advertising: Governments, car manufacturers, and environmental organizations create ads that highlight the benefits of low-emission vehicles. These ads may appear in TV commercials, billboards, social media posts, or print advertisements.
- Marketing Materials: Car dealerships may provide brochures or other marketing materials that explain how low-emission vehicles work and what their benefits are.
- Test Drives: Some dealerships offer test drives of low-emission vehicles so that consumers can experience them firsthand.
- Incentive Programs: Governments offer incentives such as tax credits or rebates for purchasing a low-emission vehicle.
By raising awareness about low emission vehicles, these campaigns help consumers understand the environmental benefits of driving one. They also encourage people to consider buying a more environmentally friendly vehicle when it’s time to purchase a new car.
Tax Incentives And Rebates
As someone interested in vehicle emissions laws and their impact, it’s important to be aware of the government policies and incentives that encourage consumers to purchase low emission vehicles. Here are some key tax incentives and rebates available:
- Federal Tax Credits: The federal government offers tax credits for qualifying plug-in electric vehicles (EVs) based on battery capacity. These tax credits can range from $2,500 to $7,500 per vehicle purchased.
- State Tax Credits: Many states offer additional tax credits on top of the federal tax credits for purchasing low emission vehicles. For example, California offers a state rebate of up to $2,500 for eligible EV purchases.
- HOV Lane Access: Some states allow low emission vehicles to use the High Occupancy Vehicle (HOV) lanes regardless of the number of passengers in the car.
- Local Incentives: Many cities and municipalities offer incentives such as free parking or charging station access for owners of low emission vehicles.
By taking advantage of these incentives and rebates, consumers can not only save money on their vehicle purchase but also contribute towards a cleaner environment by driving a low emission vehicle.
Conclusion
Low emission vehicles, also known as LEVs, play an essential role in reducing air pollution and conserving natural resources. These vehicles use advanced technology to limit greenhouse gas emissions while providing a comfortable driving experience.
As the world becomes more environmentally conscious, low emission cars are increasingly becoming the norm for consumers searching for reliable and sustainable options. Governments worldwide have adopted policies and incentives to promote low-emission vehicle use by offering tax credits, rebates, and public awareness campaigns.
By choosing an LEV instead of traditional gasoline-powered transportation, individuals can help preserve our planet’s health for generations to come.
FAQs:
What is a low emission vehicle?
A low emission vehicle is a car, truck or other mode of transportation that releases fewer pollutants into the air than traditional combustion engine vehicles.
Why are low emission vehicles important for the environment?
Low emission vehicles help reduce pollution and improve air quality by emitting fewer harmful gases like carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides and particulate matter that contribute to climate change. They also use less fuel and produce less noise pollution.
How do low emission vehicles work?
Some types of low emission vehicles use alternative power sources such as electric batteries or hydrogen fuel cells to power their engines instead of gasoline or diesel fuel used in conventional cars. Others have specialized technology designed to limit emissions and more efficiently use traditional fossil fuels.
Are there any government incentives for purchasing a low emission vehicle?
Yes, many governments offer incentives such as tax credits, rebates or exemptions on sales tax for drivers who purchase low-emission cars based on specific criteria – usually related to efficiency ratings or the type of power source used (e.g., electric vs hybrid). These initiatives encourage consumers to buy cleaner alternatives while helping cut down on greenhouse gas emissions from daily commutes and travel overall.
- Tesla Charger Installation Cost (Home Setups) - March 1, 2024
- Tesla Phone Key Disconnected (Troubleshooting Guide and Quick Fixes) - March 1, 2024
- Tesla FSD 12 (Explained) - March 1, 2024