Understanding Electric Vehicle Emissions
Electric vehicles such as battery-electric vehicles and hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicles, produce zero tailpipe emissions, setting them apart from gasoline cars and highlighting their potential as a greener alternative.
These zero tailpipe emissions vehicles are classified as “zero-emission vehicles” (ZEVs).

Electric vehicles and tailpipe emissions
Electric vehicles (EVs) drastically cut tailpipe emissions in the environment, a benefit with significant environmental and health implications.
Traditional gasoline-powered cars release various pollutants, including greenhouse gases and harmful nitrogen oxides directly into the air we breathe through their exhaust systems.
On the contrary, EVs are designed in such a way that they have no exhaust system thus generating zero tailpipe emissions when driven.
This characteristic makes them an ideal solution in densely populated urban areas where air quality can be particularly low due to high levels of vehicular pollution.
Nevertheless, while EVs’ operational phase is indeed emission-free, it’s worth noting the whole life cycle emissions including those from electricity generation for charging EVs which may vary based on the power source used.
Comparing emissions to fossil fuel and hydrogen vehicles
It’s important to compare the emissions of electric vehicles with those of traditional fossil fuel-powered vehicles and hydrogen vehicles to fully understand their environmental impact.
| Vehicle Type | Emissions during operation | Emissions during fuel/energy production |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Electric Vehicles | Zero tailpipe emissions | Emissions depend on the source of electricity, with possible pollution from power plants |
| Fossil Fuel Vehicles | Significant emissions, including CO2 and other greenhouse gases | Considerable emissions from oil extraction, refining, and fuel combustion |
| Hydrogen Vehicles | No harmful emissions on the road | CO2 released during hydrogen production, which typically involves natural gas or water |
This comparison shows that both electric and hydrogen vehicles present fewer emissions during operation than fossil fuel vehicles. However, they do generate emissions during the energy production stage.
The type and quantity of these emissions can vary widely depending on factors such as the source of electricity for electric vehicles and the method of hydrogen production for hydrogen vehicles.
Conversely, fossil fuel vehicles produce substantial emissions both during operation and fuel production. As a result, the transition to electric and hydrogen vehicles can help reduce the overall carbon footprint of the transportation sector.
Factors Affecting Electric Vehicle Emissions
Electric vehicle emissions can be influenced by several factors, including the emissions generated in the manufacturing process, the disposal and recycling of batteries, and the overall life cycle emissions.
Manufacturing process emissions
Electric vehicles (EVs) indeed fall under the zero-emission category when considering tailpipe emissions, however, their manufacturing process tells a different story.
The production of EVs, specifically the assembly and manufacturing of batteries, often contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.
About half these emissions result from the electricity required in this energy-intensive procedure.
Furthermore, battery production can add an extra 30% to 40% to the overall vehicle’s emissions depending on its location of manufacture — primarily due to differences in energy production methods across countries.
Driven by this fact, much debate concentrates around whether electric cars are genuinely more eco-friendly than their fossil fuel-powered counterparts despite higher initial emission costs.
It is nevertheless crucial to address that over an EV’s lifecycle – including manufacture, use and disposal – they typically remain greener alternatives compared with gasoline cars thanks largely due to lower operating emissions and potential for renewable charging sources.

Battery disposal and recycling
Proper battery disposal and recycling are crucial steps in minimizing environmental pollution and addressing sustainability challenges associated with electric vehicles (EVs). As the adoption of EVs continues to grow, ensuring the responsible management of their batteries becomes increasingly important.
Fortunately, there are ongoing efforts to develop efficient recycling methods. In fact, the United States currently leads the world in lithium-ion battery recycling, utilizing both pyro- and hydrometallurgical techniques.
Recycling not only helps reduce emissions associated with manufacturing new batteries but also addresses concerns about waste management and contributes to a more sustainable future.
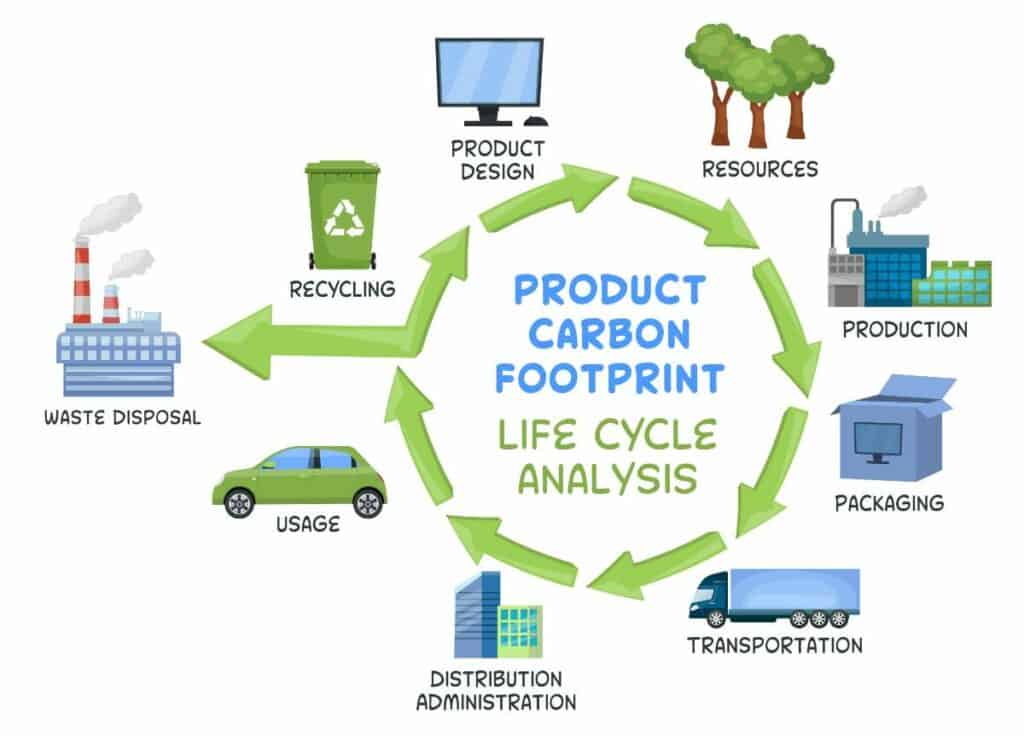
Life cycle emissions
Electric vehicles (EVs) have garnered attention for their lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
However, it’s important to consider the full life cycle emissions of EVs, which include their manufacturing process, battery disposal and recycling, as well as ongoing energy consumption.
Life cycle analysis takes into account all these factors to evaluate the overall climate impact of electric vehicles.
Studies have shown that despite some emissions associated with production and disposal, the total life-cycle emissions of hybrid and electric vehicles can be up to 89% lower than those of internal combustion engine vehicles.
This makes EVs a greener choice when it comes to reducing carbon footprints and combating climate change.
The Environmental Impact of Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles have a profound environmental impact, as they significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve air quality, and contribute to the integration of renewable energy sources.
Reduced greenhouse gas emissions
Electric vehicles are making a significant difference in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. According to studies, electric cars emit fewer greenhouse gases and air pollutants compared to traditional petrol or diesel cars.
In fact, research has shown that over their lifetime, electric vehicles typically have lower greenhouse gas emissions than gasoline-powered vehicles.
Additionally, a report by the European Environment Agency revealed that electric vehicle emissions were about 17-30% lower than those of petrol and diesel vehicles.
This reduction in greenhouse gas emissions is crucial for combating climate change and creating a more sustainable future.
Positive impact on air quality
Electric vehicles have a significant positive impact on air quality. Unlike conventional cars powered by fossil fuels, electric cars produce zero tailpipe emissions. This means that they do not release any harmful pollutants into the atmosphere while driving.
As a result, the air we breathe becomes cleaner and healthier for everyone. Studies have shown that adopting electric vehicles can lead to reduced air pollution, which in turn improves respiratory health and reduces the risk of related diseases.
By transitioning to electric cars, we can make a substantial difference in improving urban air quality and creating a more sustainable environment for future generations.

Contribution to renewable energy integration
Electric vehicles (EVs) have the potential to play a significant role in integrating renewable energy sources into our transportation system. By charging EVs with electricity from renewable sources such as wind, solar, or hydro power, we can reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and decrease greenhouse gas emissions.
In fact, studies have shown that EVs powered by low-emitting electricity sources can cut environmental health impacts by more than 50% compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
This means that as the adoption of EVs continues to grow and renewable energy becomes more prevalent, our transportation sector can become cleaner and more sustainable.
Government policies are also being implemented to support the integration of renewable energy and electric vehicles, recognizing their potential positive impact on both the environment and our overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electric vehicles are not completely zero emission, but they have significantly lower emissions compared to traditional gasoline cars. While there may be emissions associated with the manufacturing process and battery disposal, their overall environmental impact is still far less than that of fossil fuel vehicles.
Electric cars play a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving air quality, and promoting renewable energy integration. So while they may not be entirely emission-free, electric vehicles are undoubtedly a greener and more sustainable option for our future transportation needs.
FAQs
1. Are electric vehicles truly zero emission?
Yes, electric vehicles (EVs) are considered to be zero emission vehicles because they do not emit any tailpipe pollutants when running on electricity.
However, it’s important to note that emissions can still be produced during the generation of electricity used to charge the vehicle.
2. What about the environmental impact of producing EV batteries?
While EVs produce zero emissions during operation, there are environmental considerations related to the production and disposal of their batteries.
The mining and processing of materials for battery production can have an impact on ecosystems if not done sustainably. However, advancements are being made in battery technology and recycling processes to minimize these impacts.
3. How do electric vehicles compare to gasoline-powered cars in terms of overall emissions?
Electric vehicles have lower overall emissions compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars when considering the full life cycle of both types of vehicles, including manufacturing, driving, and disposal phases.
This is due to EVs’ higher energy efficiency and a shift towards cleaner sources of electricity generation.
4. Are there any benefits other than reduced emissions from using electric vehicles?
Yes, apart from reduced emissions, electric vehicles offer several additional benefits such as lower operating costs (as electricity prices are generally more stable than fuel prices), quieter operation (reduced noise pollution), potential government incentives or tax credits for purchasing an EV, and improved energy security by reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
- Tesla Charger Installation Cost (Home Setups) - March 1, 2024
- Tesla Phone Key Disconnected (Troubleshooting Guide and Quick Fixes) - March 1, 2024
- Tesla FSD 12 (Explained) - March 1, 2024